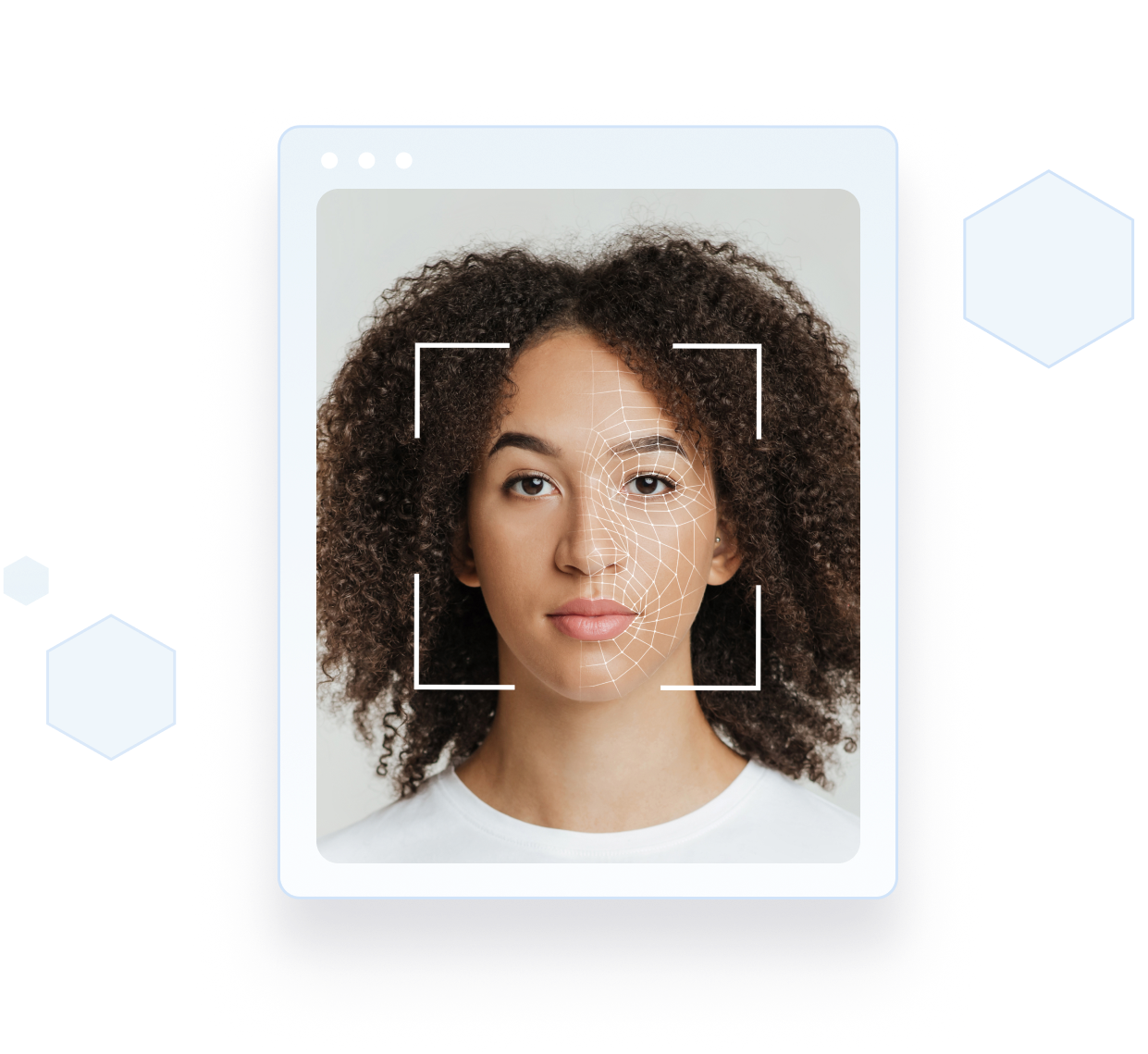
Effortless and accurate patient identification
Using biometric facial recognition technology ensures accurate patient identification, reduces claims denial, streamlines check-in, and enhances safety and care.
Manual identification processes aren’t cutting it
Traditional patient identification processes too often result in misidentification and are needlessly burdensome.
Imprivata Patient Access uses advanced face authentication to capture biological characteristics. It significantly increases identification accuracy, reduces the risk of errors and related costs, all while improving the patient experience.
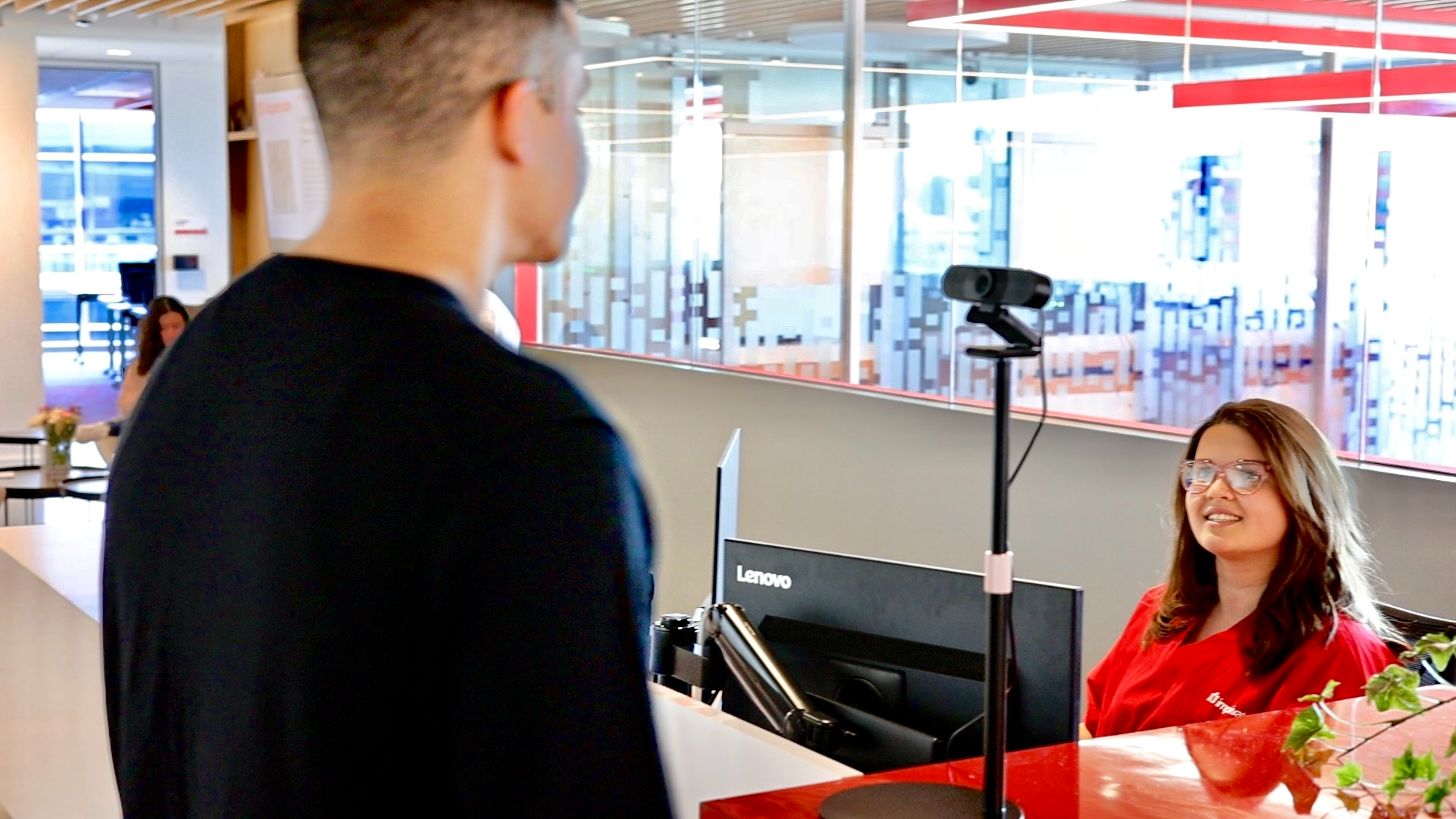

Benefits of moving to biometric patient identification
Reduce the risk of medical error by ensuring clinicians have accurate and complete patient information

Accurate patient identification reduces billing errors and claims denials
Reduce patient wait times during enrollment and check-in
Stop wasting valuable staff time remedying duplicate patient records
Frequently asked questions
Skip list contentHow does the solution work?
Is the technology accurate even if patients wear glasses, a mask, or a hat?
Does the solution require expensive hardware or cameras?
How do you use and protect patient biometric data?